

This may include questions about medical history, communication concerns, and symptoms that are experienced. Additionally, a Pre-Appointment Questionnaire will be e-mailed to complete prior to the appointment. An Audiologist will review any records if the test was completed at another facility to ensure it meets our standards. If a hearing test has not been completed within 6 months of the APD evaluation appointment, this will need to be scheduled. Your appointment will be confirmed 24 hours prior to the evaluation date.
Difficulty understanding intonation of speech (for example, understanding sarcasm, idioms, or jokes).Frequent requests for repetition or rephrasing of instructions.
#Auditory processing disorder treatment series
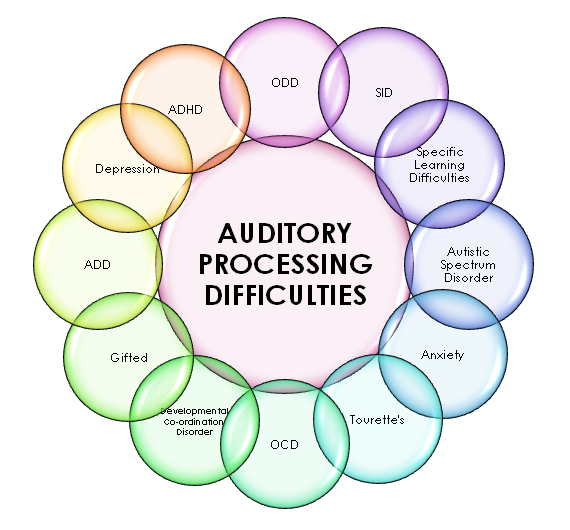
Difficulty following a series of directions (for example, when using “first”, “next”, “afterwards”, etc.).Reports of not hearing well, despite being diagnosed with normal hearing.Signs and symptoms can present themselves differently, depending on age. Symptoms typically appear at a young age and can range from mild to severe. In patients with APD, hearing thresholds are often normal, but the central nervous system has trouble processing what is being heard. In essence, APD is a learning and social-communication disability, not a hearing problem. What are signs and symptoms for Auditory Processing Disorder? The disorder can affect anyone but is estimated to appear in as many as 5 to 7 percent of school-age children, according to the Auditory Processing Disorder Foundation, with boys diagnosed twice as often as girls. Understanding speech with background noise or when the speech signal is not clear.Sound Localization (telling where a sound is coming from).Binaural Processing (separating and integrating different signals from each ear at the same time).Temporal Processing (deciphering gaps and rates of speech appropriately).Discriminating Auditory Stimuli (telling different sounds apart).More specifically, these functions include: APD can affect the functions to refine, analyze, modify, organize information that our ears send to the brain. Auditory processing disorder (APD), a neurological condition also known as central auditory processing disorder (CAPD), affects the brain’s ability to process auditory input, making it difficult to understand speech, follow oral instructions, or distinguish speech in noisy environments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
